Vitamin C: immune system health and tissue repair
Vitamin C, also known as ascorbic acid, is a powerful antioxidant that helps protect our bodies from free radical damage. It is also essential for the production of collagen, a protein needed for the health of our skin, bones, tendons and blood vessels. In addition, vitamin C plays an important role in wound healing and tissue repair, which is especially important for athletes who exercise intensively on a regular basis.
Adequate intake of vitamin C can also contribute to a healthy immune system. It can help your body fight off germs and it can reduce the risk of colds and flu. This is especially important for athletes, as intense exercise can suppress the immune system and increase the risk of disease.
For athletes, adequate intake of vitamin C can also improve performance. Studies have shown that it can increase endurance and reduce recovery time after exercise. In addition, vitamin C can increase iron absorption, which can help improve oxygenation to muscles during exercise.
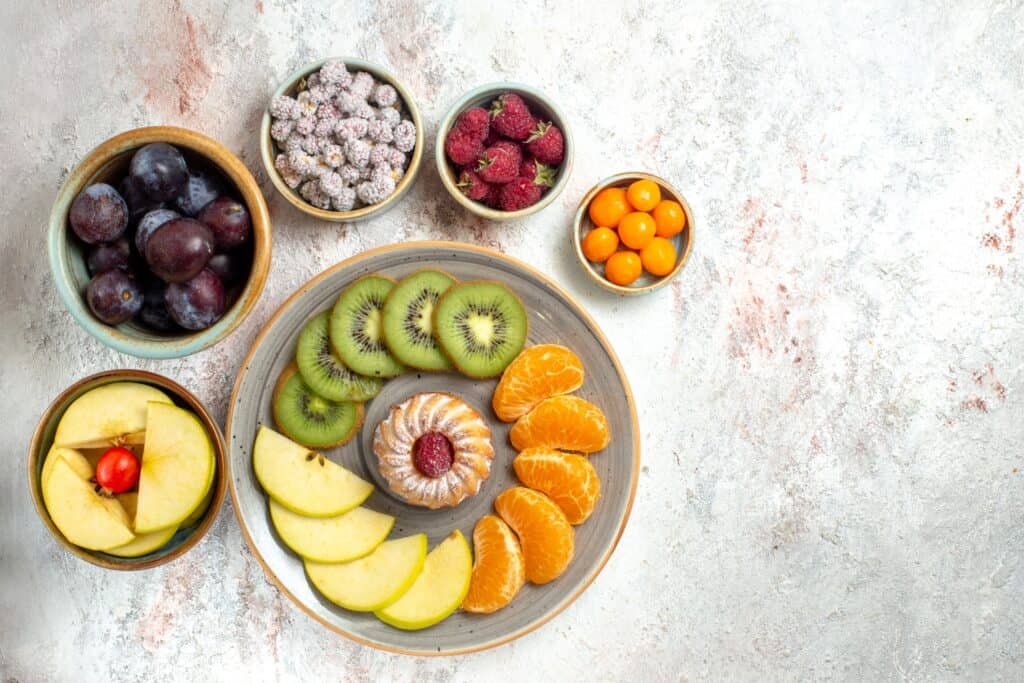
Vitamin C is found in many different foods, including citrus fruits, strawberries, peppers and spinach. It is also available in supplement form, which can be a convenient option for athletes who struggle to get enough vitamin C from their diet.
Vitamin D: For bone health and muscle function
Vitamin D is perhaps best known for its role in bone health. It helps our bodies absorb calcium, a mineral essential for the health and strength of our bones. Vitamin D deficiency can lead to decreased bone density, which can increase the risk of fractures and injuries.
In addition to its role in bone health, vitamin D also plays an important role in muscle function. Research has shown that vitamin D can help improve muscle strength and performance, which is especially important for athletes.
In addition, adequate intake of vitamin D can support the immune system. Studies have shown that it can help reduce the risk of colds and flu, which can be especially valuable for athletes who don’t want their training derailed by illness.
It is important to know that our bodies can produce vitamin D when our skin is exposed to sunlight. However, in some parts of the world, especially during the winter months, it can be difficult to get enough sunlight. In this case, it may be helpful to get vitamin D from dietary sources or supplements.