Introduction: what is eczema?
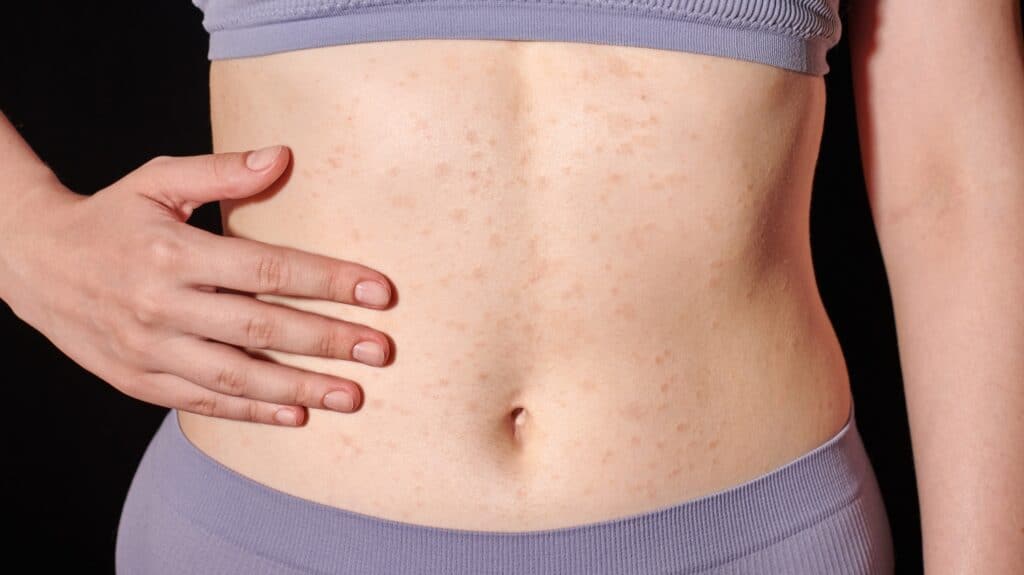
Eczema, also known as dermatitis, is a skin condition characterized mainly by itchy, red and dry skin. It can occur in different forms and degrees, ranging from mild cases to severe cases where the skin may form blisters and scabs. Eczema is extremely widespread; it affects a significant number of people regardless of age, race or gender.
Eczema is chronic in nature and may have periods of flare-ups and remissions. This means that symptoms may disappear for a period of time but may return again. It can have a significant impact on an individual’s quality of life, leading to sleep deprivation, psychological stress and reduced productivity.
Although eczema is a common condition, the experience of it remains highly subjective. The impact on daily life varies from person to person. Some people can continue their normal routine with minimal disruption, while others experience severe forms of eczema that greatly affect their daily activities.
Treatment of eczema can depend on several factors, including the patient’s age, severity of symptoms, presence of other health problems and individual response to treatment. One of the possible treatments that has received attention in recent years is the use of the probiotic bacterium Lactobacillus Rhamnosus.
What causes eczema?
To date, the exact cause of eczema is not fully understood. However, it is believed to be due to a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Genetic factors can contribute to the development of eczema by affecting the immune system, causing it to become overactive and react violently to irritants or allergens.
Environmental factors can also play a role in the development of eczema. These factors can range from exposure to certain chemicals and allergens to weather conditions and stress. Moreover, an individual’s general health condition, including the health of the digestive system, can also contribute to the development of eczema.
It has also been shown that people with eczema often have a damaged skin barrier. This means that their skin is less effective at retaining moisture and keeping out irritants and allergens. This can lead to dry, sensitive skin prone to eczema.
In addition, it is believed that eczema can be triggered or aggravated by certain foods, certain types of substances, smoke, stress, and hormonal changes. These triggers can vary from person to person.
What is Lactobacillus Rhamnosus?
Lactobacillus Rhamnosus is a type of probiotic bacteria that occurs naturally in the human body, mainly in the intestines. Probiotics are live microorganisms that, when ingested in adequate amounts, can provide health benefits to the host. They play a crucial role in the body, particularly in maintaining gut health and the immune system.
Lactobacillus Rhamnosus is one of the many species of Lactobacillus bacteria considered probiotics. It is widely recognized for its health benefits, including improving digestion, strengthening the immune system, and helping to manage certain skin conditions, such as eczema.
This bacterium is often found in fermented foods, such as yogurt and cheese. It can also be taken in the form of a supplement. It is important to note that although Lactobacillus Rhamnosus is generally safe for most people, it is advisable to consult a physician before starting any supplement.
The ability of Lactobacillus Rhamnosus to improve skin health may be due to the fact that it helps modulate the immune system and limits the growth of harmful bacteria in the intestines. By doing so, it can help manage inflammatory skin conditions such as eczema.