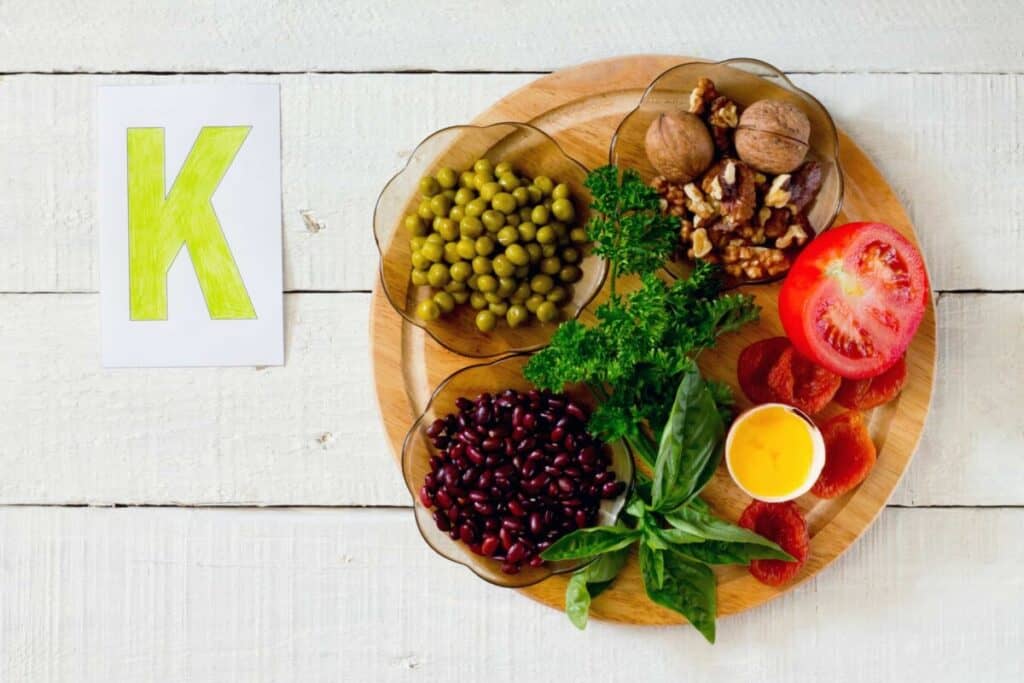
Introduction to vitamin K
Vitamin K is an essential nutrient that plays a vital role in various bodily functions. It is a fat-soluble vitamin found naturally in two forms: vitamin K1 and vitamin K2. Both forms play crucial roles in blood clotting and bone health. Understanding the importance of vitamin K and knowing its sources can help maintain optimal health.
Although vitamin K is less well known than many other vitamins, it is no less important. Like other vitamins, vitamin K plays an essential role in the body. One of the main functions of vitamin K is to help with blood clotting, allowing the body to heal after an injury. It is also involved in bone metabolism and cellular health.
Vitamin K is a fat-soluble vitamin, which means it is stored in body fat. Unlike water-soluble vitamins, which must be replenished daily because they are not stored in the body, a supply of vitamin K can be stored in the body for some time. However, that doesn’t mean you shouldn’t pay attention to your intake of vitamin K. As with all nutrients, it’s important to make sure you’re getting enough for optimal health.
The body needs vitamin K to stay healthy, but most people get enough of this vitamin from their diet. However, there are some groups of people who may not get enough vitamin K. This includes people on low-fat diets or who have digestive disorders that may affect vitamin K absorption.
The role of vitamin K in the body
Vitamin K is best known for its role in the blood clotting process. When you are injured and begin to bleed, vitamin K helps your body form a blood clot to stop the bleeding. It does this by contributing to the production of four of the 13 proteins required for blood clotting.
But vitamin K’s role in the body goes beyond blood clotting. Research has shown that vitamin K also plays an important role in maintaining strong bones. It helps regulate calcium in the body, which is crucial for bone health. People with low levels of vitamin K may have a higher risk of bone fracture.
Vitamin K has also been linked to heart health. Studies have shown that people with low levels of vitamin K may be at greater risk for heart disease. This is because vitamin K helps keep calcium in the bones and prevent it from accumulating in the blood vessels.
In addition, vitamin K plays a role in cell growth and function. It is involved in the production of certain proteins essential for cellular health and function. This means that vitamin K can help promote overall health at the cellular level.